Fundamental Theorem of Linear Algebra
A matrix $\mathbf{A}\in\mathbb{C}^{3\times 2}_{\rho}$, induces a row space and a column space with the orthogonal decomposition:
$$
\begin{align}
%
\mathbf{C}^{2} =
\color{blue}{\mathcal{R} \left( \mathbf{A}^{*} \right)} \oplus
\color{red}{\mathcal{N} \left( \mathbf{A} \right)} \\
%
\mathbf{C}^{3} =
\color{blue}{\mathcal{R} \left( \mathbf{A} \right)} \oplus
\color{red} {\mathcal{N} \left( \mathbf{A}^{*} \right)}
%
\end{align}
$$
Method of least squares
Given an appropriate data vector $b\in\mathbb{C}^{3}$, the linear system
$$
\mathbf{A} x = b
$$
has a least squares solution defined by
$$
x_{LS} = \left\{
x\in\mathbb{C}^{2} \colon
\big\lVert
\mathbf{A} x - b
\big\rVert_{2}^{2}
\text{ is minimized}
\right\}
$$
The least squares solution is computed using
$$
x_{LS} =
\color{blue}{\mathbf{A}^{+} b} +
\color{red}{
\left(
\mathbf{I}_{n} - \mathbf{A}^{+} \mathbf{A}
\right) y}, \quad y \in \mathbb{C}^{n}
\tag{1}
$$
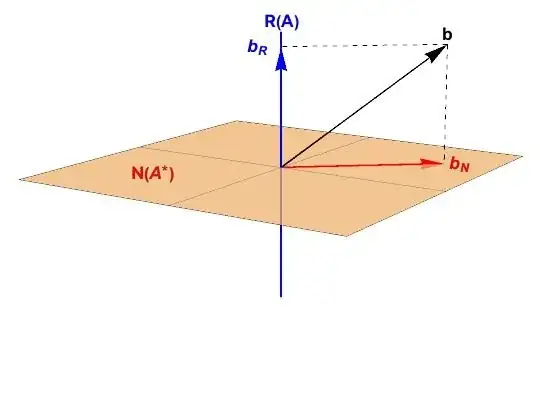
Decomposing the data vector
The least squares solution resolves the data vector into $\color{blue}{range}$ and $\color{red}{spaces}$ as
$$
b = \color{blue}{b_{\mathcal{R}}} + \color{red}{b_{\mathcal{N}}}
$$
The portion of the data vector in the range space is
$$
\color{blue}{x_{LS}} =
\color{blue}{\mathbf{A}^{+}b} =
\color{blue}{b_{\mathcal{R}}}
$$
Read a bit more: How does minimum squared error relate to a linear system?, Finding the null space of a matrix by least squares optimization?
To draw specific diagrams, pick the case where the rank of the matrix is $\rho=1$.
Column space
The minimization occurs in the column space.
Row space
The set of least squares minimizers in (1) is an affine space, represented by the dashed red line in the figure below.
The operator $\color{red}{
\left(
\mathbf{I}_{n} - \mathbf{A}^{+} \mathbf{A}
\right) y}$ projects the vector $y$ onto the null space $\color{red}{\mathcal{N} \left( \mathbf{A} \right)}$.
The blue point $\color{blue}{x_{LS}}$ is the pseudoinverse solution
$$
\color{blue}{x_{LS}} =
\color{blue}{\mathbf{A}^{+}b}
$$
and is the solution of the minimum norm. This is where the affine space of the least squares minimizers $x_{LS}$ intersects the range space, $\color{blue}{\mathcal{R} \left( \mathbf{A}^{*} \right)}$.


