I'm given the system of equations $x'(t) = -2y + x^2$, $y\,'(t) = 4x - 2y$, and I am supposed to find all steady state solutions. Once I find them, I need to determine what kind of steady states I have (sink, source, etc.). I'm having a lot of trouble with this chapter so I have no idea. Can you please explain the answer to me? Also what is a steady state solution and what is a steady state?
-
Are you sure you have $x^2$ in the first equation? – Mhenni Benghorbal May 07 '13 at 06:22
-
yes, it is nonlinear. – Sara May 07 '13 at 06:31
-
Did this problem come from applications or you are studying differential equations now? – Mhenni Benghorbal May 07 '13 at 06:38
-
we are going over it right now in a differential equations course. – Sara May 07 '13 at 06:40
-
I'm an undergrad T.A., and the students in the course are doing this stuff right now. My first concern is that I'm just not familiar with steady state solutions and state states (are they just equilibrium points?). – Sara May 07 '13 at 06:56
2 Answers
We are given:
$$f(x, y) = x'(t) = -2y + x^2$$ $$g(x, y) = y'(t) = 4x - 2y$$
We solve for the critical points by finding the simultaneous point where $x'$ and $y'$ both equal zero, so you found those points as: $(0,0)$ and $(4,8)$.
Next, we find the Jacobian matrix of the system as:
$$\displaystyle J(x,y) = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial f}{\partial y}\\\frac{\partial g}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial g}{\partial y}\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}2x & -2\\4 & -2\end{bmatrix}$$
Now, we evaluate the eigenvalues at the two critical points using the Jacobian matrix $J(x,y)$, so we have:
$$\displaystyle J(0,0) = \begin{bmatrix}0 & -2\\4 & -2\end{bmatrix}$$
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the CP $(0,0)$ yield:
- $\lambda_1 = ~~i (\sqrt 7+i), ~v_1 = \left(\dfrac{1}{4}(1+i \sqrt 7), 1\right)$
- $\lambda_2 = -i (\sqrt 7-i), ~v_2 = \left(\dfrac{1}{4} (1-i \sqrt 7), 1\right)$
- These are complex conjugate eigenvalues with negative real part $\rightarrow$ stable spiral (node).
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the CP $(4,8)$ yield:
$$\displaystyle J(4,8) = \begin{bmatrix}8 & -2\\4 & -2\end{bmatrix}$$
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the CP $(0,0)$ yield:
- $\lambda_1 = ~~3+ \sqrt {17}, ~v_1 = \left(\dfrac{1}{4} (5+ \sqrt {17}), 1\right)$
- $\lambda_2 = 3- \sqrt {17}, ~v_2 = \left(\dfrac{1}{4} (5- \sqrt {17}), 1\right)$
- These are real eigenvalues with positive and negative $\rightarrow$ unstable saddle point.
We can draw a phase portrait to show this behavior over time as:
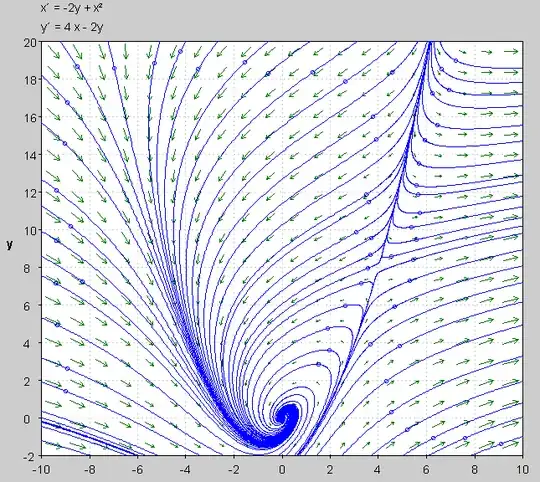
Notice the analytical result at the two critical points.
We can also write the solution to these expressions as functions of time, but the phase portrait shows the local and global behavior over time.
- 56,629
Steady state problems are time independent problems. So, in the case where we want a steady state solution, we are basically looking for solutions that won't change when the time progresses. In practice, to find the steady state, we require the derivative to be zero. So, in your case, you will have to solve the system
$$ x^2-2y=0 $$
$$4x-2y=0 . $$
- 7,647
- 48,099
-
Okay, I got points $(0,0)$ and $(4,8)$. So is it correct to say that $(x,y)=(0,0)$ and $(x,y)=(4,8)$ are steady state solutions? – Sara May 07 '13 at 07:32