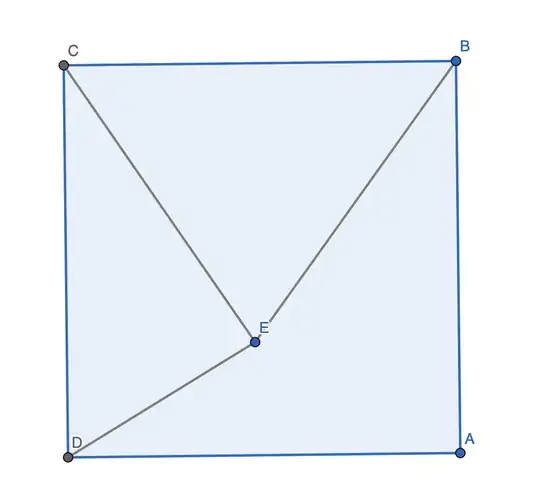
A solution for any E in square ABCD
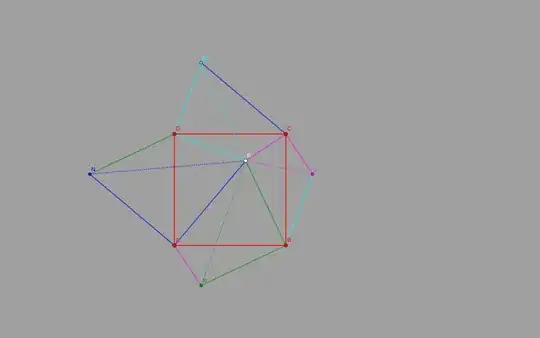
Picture has the triangles the square is composed of appended to the sides.
Let a (blue) b (green) c (magenta) d (cyan) be the distances from any interior point E to the vertices A B C D of the square.
The total area $O$ of the octagon is twice the area of the square.
There are four mono color (blue, green, magenta, cyan) orthogonal equilateral triangles contributing:
(1) $$\frac{a^2+b^2+c^2+d^2}{2}$$
to the total area of the octagon.
The remaining contributing four three color triangles have one of the sides (shown dotted) a distance multiplied by $\sqrt{2}$.
The side lengths $$(x,y,z)$$ of these four triangles are equal to $$(a,\sqrt{2}b,c)$$ $$(b,\sqrt{2}c,d)$$ $$(c,\sqrt{2}d,a)$$ $$(d,\sqrt{2}a,b)$$ and their areas can be computed by Heron's formula:
(2) $$\sqrt{s(s-x)(s-y)(s-z)}$$ where $$s = \frac{x+y+z}{2}$$
So now we can sum up total octagon area $O$ and the square side is:
(3) $$\sqrt(\frac{O}{2})$$
But: $d$ is a function of $(a,b,c)$ :
(4) $$d(a,b,c)=\sqrt{a^2-b^2+c^2}$$
[where one chooses a b c correctly a>=b>=c]
This is not hard to prove [draw lines through E parallel to square sides and use Pythagoras].
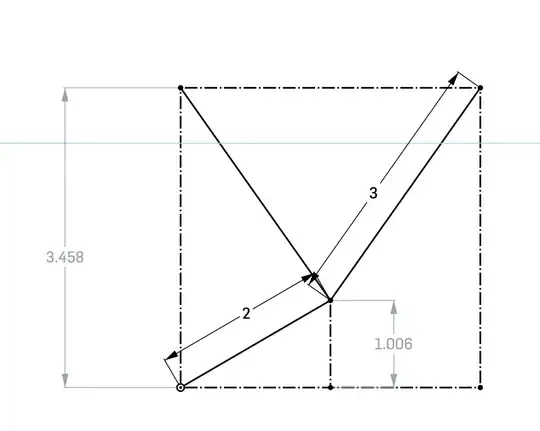
Below Julia code tests an OP @BarSmith answer example case where $CE=3$ and $DE=2$ giving expected square side rounded $3.458$.
Combining (1) and (2) and (3) and (4) allows to explicitly write a formula (as is implicitly done in code).
# Heron formula for triangle area
# given triangle sides
function H(a,b,c)
s = (a + b + c) / 2
return sqrt(s * (s - a) * (s - b) * (s - c))
end
side length of square ABCD given distances a b c d
from interior point E to vertices
function L(a,b,c,d)
# 4 orthogonal equilateral triangles
surface =
((a^2 + b^2 + c^2 + d^2) / 2) +
# 4 extra tricolor triangles with one side * sqrt(2)
H(a, sqrt(2) * b, c) +
H(b, sqrt(2) * c, d) +
H(c, sqrt(2) * d, a) +
H(d, sqrt(2) * a, b)
# surface is twice square surface
# side length is square root
return sqrt(surface / 2)
end
distances d to vertex D of square ABCD
given distances a b c
from interior point E to vertices A B C
D(a, b, c) = sqrt(a^2 - b^2 + c^2)
side length of square ABCD given distances a b c
from interior point E to vertices A B C
a >= b >= c
function L(a,b,c)
return L(a, b, c, D(a, b, c))
end
3 3 2 example
a = 3
b = 3
c = 2
d = 2
println(L(a,b,c))
exit(0)
$ julia Julia/abcde.jl
3.457507202786114