Suppose that $X$ is a finite set, and that $\mathcal{P}(X)$ is the powerset of $X$. Suppose we uniformly sample two sets $A,B \in \mathcal{P}(X)$. What is the probability that $A \subseteq B$?
I ran the following simulation:
from itertools import chain, combinations
from random import sample
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def powerset(iterable):
s = list(iterable)
return chain.from_iterable(combinations(s, r) for r in range(len(s)+1))
pX = [set(i) for i in powerset(list(range(10)))]
results = []
N = 1000
for k in range(10000):
count = 0
for i in range(N):
A,B = sample(pX, 2)
if A.issubset(B):
count += 1
else:
continue
results.append(count / N)
plt.hist(results, bins=100)
plt.show()
This produces the following histogram of the estimates of this probability:
So the probability seems to be about 5-6 percent. Does this have an exact answer if we know the (finite) number of elements in $X$?
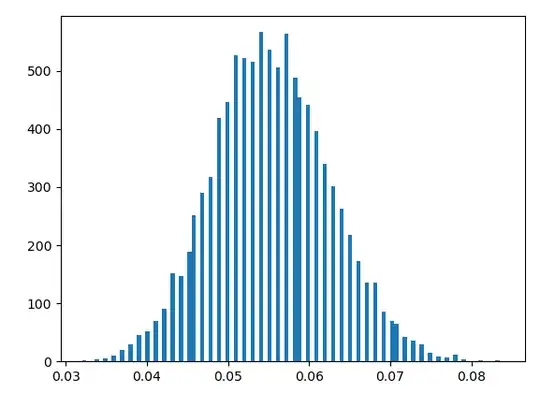
3 ** 10 / (2 ** 10) ** 2evaluates to0.056313514709472656in Python, so that seems about right. – Galen May 15 '22 at 06:56(3/4) ** 10also evaluates to0.056313514709472656. – Galen May 15 '22 at 06:57