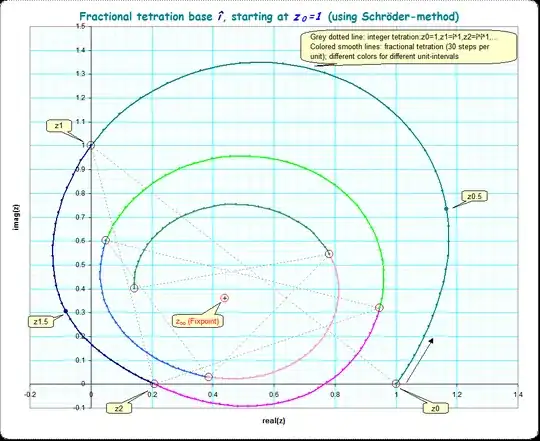
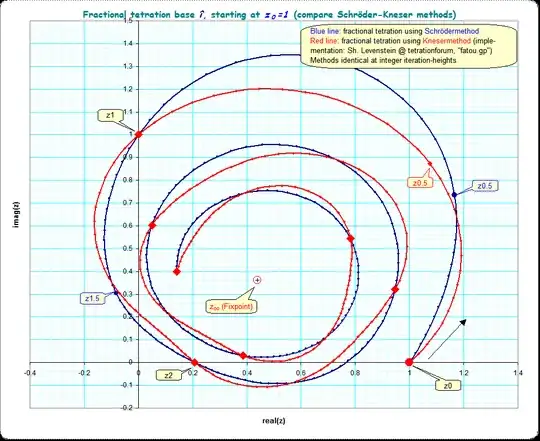
As Gottfried hints, there is yet another solution to $^{0.5}i \approx 1.07571355731 + 0.873217399108i$
I will use this question to describe a unique Abel function for $f(z)=i^z$. I wrote a pari-gp complex base tetration program available for download at math.eretrandre.org. The results posted here were generated with that program. I will use this question about base(i) to show that if there is a solution of this type, than it has to be unique. This tetration can be regarded as an extension of Kneser's solution for real bases>$\exp(\frac{1}{e})$, to tetration for complex bases. So what is "this type" of complex base slog/abel function solution?
The answer is this Abel function involves both primary fixed points. The op points out the attracting fixed point, $l_1 \approx 0.438282936727 + 0.360592471871i\;$. There is also a repelling fixed point $l_2 \approx -1.86174307501 - 0.410799968836i\;$. Henryk Trapmann's uniqueness criteria
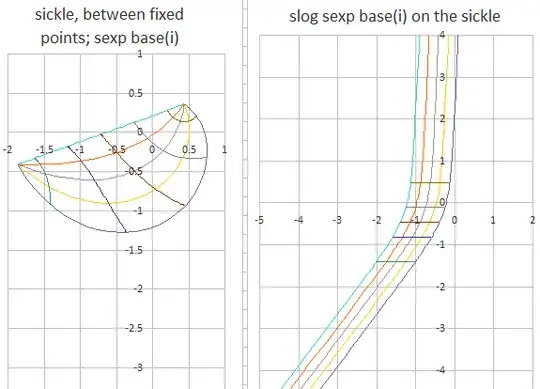
says if you can make a sickle between the two fixed points, bounded on one side by a defined curve f(z), and bounded on the other side by $i^{f(z)}$. For sexp base(i), we can choose f(z) as a straight line between the primary fixed points. Henryk's proof says if there is a one to one analytic mapping between the sickle, and the Abel function, excluding the two fixed points, and if the derivative of the Abel function is never zero, than it is unique to an additive constant. The additive constant is uniquely determined by the requirement that Tetration have the slog(1)=abel(1)=0.
Here is a picture of the sickle, and $\alpha(z)$ or the abel/slog on the sickel. You can see the one-to-one mapping between the two fixed points, extending between $-\Im \infty$ and $+\Im \infty$. The mapping between the straight line, and f(z) are always be definition exactly one cycle apart, since $\alpha(f(z))=\alpha(z)+1$. I also filled in vertical grid lines for sexp(z+0.25), sexp(z+0.5) and sexp(z+0.75). The two graphs are colored identical to allow visual verification of the one to one mapping. Because $\exp_i(z)$ is well defined, the sexp(z) function can be extended to the right over the entire complex plane, and extended to the left except for logarithmic branch singularities. So this slog on a sickle defines sexp(z) base(i) for the entire complex plane! Henryk Trapmann's uniqueness proof generates a mapping function between this solution and the other purported solution. Since both functions are analytic on the strip, it turns out both the mapping function and its inverse have to be entire, which can only be the case if the two slogs are the same except for an additive constant.
Near the attracting fixed point, the function approaches arbitrarily closely to the attracting fixed point Abel/Schroeder function, and near the repelling fixed point, the function approaches the repelling fixed point Abel/Schroeder function.
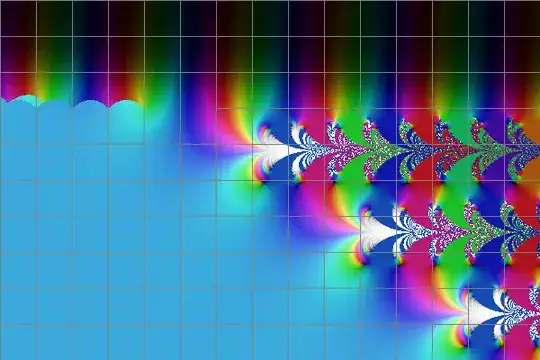
sexp base i in the complex plane, grids are 1 unit apart. You can see the logarithmic singularity at z=-2.
The Abel function Taylor series was computed using the following form:
$$\alpha(z)=\frac{\ln(z-l_1)}{\ln(\lambda_1)} + \frac{\ln(z-l_2)}{\ln(\lambda_2)} + p(z)$$
$\lambda_1$ and $\lambda_2$ are the multipliers at the two fixed points, $l_1$ and $l_2$,
$$i^{l_1+z} = l_1 + \lambda_1 \cdot z + a_2 \cdot z^2 + a_3 \cdot z^3...$$
It turns out $p(z)$ has a relatively mild singularity at each of the two fixed points when this form is used for the Abel/slog function. For example, $p(z)$ and its derivative are both continuous and differentiable at both of the two fixed points, although the 3rd and higher derivatives are not continuous, since the periodicity at the two fixed points is less than 3.
The pari-gp fatou.gp complex base sexp program would be used as follows:
\r fatou.gp
setmaxconvergence(); /* base i is poorly behaved */
sexpinit(i);
sexp(0.5)
1.07571355731392 + 0.873217399108003*I
Here are numerical values for $l_1, l_2, r_1=\frac{1}{\ln(\lambda_1)}$, $r_2=\frac{1}{\ln(\lambda_1)}$, and p(z), and equation for the slogestimation. The radius of convergence for p(z) is $|\frac{l1-l2}{2}|$, centered between the fixed points.
l1 = 0.4382829367270321116269751636 + 0.3605924718713854859529405269*I;
l2 = -1.861743075013160391397055791 - 0.4107999688363923093542478071*I;
r1 = -0.02244005259030164710115539234 - 0.4414842544742195824980579384*I;
r2 = 0.3613567874856575121871741974 + 0.4459440823588587557573111438*I;
slogest(z) = {
z = r1*(log(I*(z-l1))-Pi*I/2) + r2*(log(-I*(z-l2))+Pi*I/2) +
subst(p,x,(z-0.5*(l1+l2)));
return(z);
}
{p= -0.06582860911769610907611153624 - 0.6391834058813427803550150237*I
+x^ 1* ( 0.0004701290774740458290098771596 - 0.04537158729375693129580356342*I)
+x^ 2* (-0.003324372336079859782821095201 + 0.001495132937745569349230811243*I)
+x^ 3* ( 0.0007980787520098490845820065316 - 0.001533441799004958947560304185*I)
+x^ 4* (-0.001108786744422696031980666816 - 2.731877902187453470989686831 E-6*I)
+x^ 5* ( 0.0001798802115603965459766944797 + 0.0001776744851391085901363383617*I)
+x^ 6* (-0.0001598048157256642978352955851 - 3.381203527058705270044424867 E-5*I)
+x^ 7* ( 4.834500417029476499351747515 E-5 + 7.971199385246578717457250724 E-5*I)
+x^ 8* (-2.079867322054674351760533351 E-5 - 1.406842037326640069256998532 E-5*I)
+x^ 9* ( 1.690770367738385075341590185 E-5 + 2.135309134452918173269411762 E-5*I)
+x^10* (-3.353412252728033524441156034 E-6 - 5.845155821267264231283805042 E-6*I)
+x^11* ( 6.565965239846111713090140941 E-6 + 4.769875342842561685863158675 E-6*I)
+x^12* (-1.296330399893039321872277846 E-6 - 2.456868593278006094540299988 E-6*I)
+x^13* ( 2.533916981224509417637955994 E-6 + 7.218102304226136498196092124 E-7*I)
+x^14* (-8.409501999009543726430092781 E-7 - 9.279879295518162345796637972 E-7*I)
+x^15* ( 9.275250588492317644336514121 E-7 - 9.631817386499723279878826279 E-8*I)
+x^16* (-5.215083989292973029369039510 E-7 - 2.615530503953161606154084492 E-7*I)
+x^17* ( 3.116111111914753868488936298 E-7 - 1.665350480228628392912034933 E-7*I)
+x^18* (-2.781400382567721610094378621 E-7 - 1.112607415413251118507915520 E-8*I)
+x^19* ( 9.051635326999330520247332230 E-8 - 1.085008978701155103767460830 E-7*I)
+x^20* (-1.238964597578335282733301968 E-7 + 5.485260567253507938012071652 E-8*I)
+x^21* ( 1.846113879795222761048581419 E-8 - 5.632856406052825347059503708 E-8*I)
+x^22* (-4.197980145789475821721904427 E-8 + 5.240770851948157536559348001 E-8*I)
+x^23* (-1.428548543349343274791836858 E-9 - 2.602689861858463106421605234 E-8*I)
+x^24* (-6.065810598994532136326922961 E-9 + 3.328188440463381773510055778 E-8*I)
+x^25* (-4.925408783783587354755417128 E-9 - 1.098256950809547844459017995 E-8*I)
+x^26* ( 5.571041113925408468110396754 E-9 + 1.638316780708641282846896470 E-8*I)
+x^27* (-4.149193648847472629362625045 E-9 - 4.116268895249720851777701930 E-9*I)
+x^28* ( 6.721271351954440168744328856 E-9 + 5.947866395141685553477517779 E-9*I)
+x^29* (-2.739160795070694522203609350 E-9 - 1.172354292086004770247804721 E-9*I)
+x^30* ( 4.623071483414304725202549852 E-9 + 9.232228309095999063811309141 E-10*I)
+x^31* (-1.585766089923197553788716462 E-9 - 1.651307950491239271118345156 E-11*I)
+x^32* ( 2.363704675846105632188520360 E-9 - 8.296748095830550218237145087 E-10*I)
+x^33* (-8.032209583204614846555211647 E-10 + 3.448796470634182196661522301 E-10*I)
+x^34* ( 8.586697889632180390697042972 E-10 - 1.035571885972986467540525699 E-9*I)
+x^35* (-3.283321823970989260857161769 E-10 + 3.700931769620798039214959724 E-10*I)
+x^36* ( 1.060749698244576767546142485 E-10 - 7.216733126248904197113800569 E-10*I)
+x^37* (-7.435780239422554167112328213 E-11 + 2.755791031783421936772787526 E-10*I)
+x^38* (-1.572500505206983217824447542 E-10 - 3.667364964073739957874509082 E-10*I)
+x^39* ( 3.623731852785295824889239864 E-11 + 1.629657324418246834695914694 E-10*I)
+x^40* (-1.802976354364813915048318195 E-10 - 1.261880617212203404824890625 E-10*I) }