Compute the following integral:
$$\int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{e^{-x} \sin(x)}{x} dx$$
Any hint, suggestion is welcome.
Compute the following integral:
$$\int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{e^{-x} \sin(x)}{x} dx$$
Any hint, suggestion is welcome.
Yet a different approach: parametric integration. Let $$ F(\lambda)=\int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{e^{-\lambda x} \sin(x)}{x}\,dx,\qquad\lambda>0. $$ Then $$ F'(\lambda)=-\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-\lambda x} \sin(x)\,dx=-\frac{1}{1+\lambda^2}. $$ Integrating and taking into account that $\lim_{\lambda\to\infty}F(\lambda)=0$ we have $$ F(\lambda)=\frac\pi2-\arctan\lambda $$ and $$ \int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{e^{-x} \sin(x)}{x}\,dx=F(1)=\frac\pi4. $$
Using Laplace Transform, $$\mathcal{L}(\sin(x)) = \frac{1}{s^2 + 1}$$ $$\mathcal{L}\left(\frac{\sin(x)}{x}\right) = \int_r^\infty \frac{1}{s^2 + 1} ds = \frac{\pi}{2} - \arctan(r)$$ Therefore, $$\int_0^\infty e^{-rx} \frac{\sin(x)}{x} dx = \frac{\pi}{2} - \arctan(r)$$ Substituting r = 1, $$\int_0^\infty e^{-x} \frac{\sin(x)}{x} dx = \frac{\pi}{4}$$
Another approach: $$\begin{eqnarray*} \int_{0}^{\infty} dx\, \frac{e^{-x} \sin(x)}{x} &=& \int_{0}^{\infty}dx\, \frac{e^{-x}}{x} \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(-1)^k x^{2k+1}}{(2k+1)!} \\ &=& \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(-1)^k}{(2k+1)!} \int_{0}^{\infty}dx\, x^{2k} e^{-x} \\ &=& \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(-1)^k}{(2k+1)!}(2k)! \\ &=& \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(-1)^k}{2k+1} \hspace{5ex} \textrm{(Leibniz series for $\pi$)}\\ &=& \frac{\pi}{4}. \end{eqnarray*}$$
Write this as $$ \lim_{\epsilon\to0}\int_\epsilon^{1/\epsilon}\frac{e^{-(1-i)x}-e^{-(1+i)x}}{2ix}\,\mathrm{d}x\tag{1} $$ and then consider the path integral $$ \frac{1}{2i}\int_{\gamma_\epsilon} e^{-z}\,\frac{\mathrm{d}z}{z}\tag{2} $$ where $\gamma_\epsilon$ comes in along the line $(1+i)x$, makes a quarter circle clockwise along $|z|=\epsilon$, goes out along the line $(1-i)x$ and then back a quarter circle counter-clockwise along $|z|=1/\epsilon$. There are no poles inside this path, so the integral in $(2)$ is $0$.
The part along $|z|=1/\epsilon$ dies away exponentially as $\epsilon\to0$. The two parts along the lines sum to our integral, $(1)$, and the part along $|z|=\epsilon$ tends to $\frac14$ of the integral of $\frac{1}{2iz}$ clockwise around the origin; that is, $-\pi/4$. Since the sum of these parts is $0$, the limit in $(1)$ must be $\pi/4$. That is, $$ \int_0^\infty\frac{e^{-x}\sin(x)}{x}\mathrm{d}x=\frac{\pi}{4}\tag{3} $$
If you know a bit about Fourier theory. You could Parseval's theorem $$\int \!dx \,f(x) g(x)^* = \int \!d\xi\,\hat f(\xi) \hat g(\xi)^* $$ with $f(x) = \sin(x)/x$, $g(x) = \Theta(x) e^{-x}$ and $\hat{f}$, $\hat{g}$ their Fourier transforms and $\Theta(x)$ the Heaviside step function.
Hint: $\hat{f}(\xi) = \tfrac12\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}} [\Theta(1-\xi) + \Theta(1+\xi)] =\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}} \mathop{\rm rect}(\xi) $.
Let
$$f(z) = \frac{e^{-z+iz}}{z}$$
and let $C$ be the contour that travels along $0$ to $R$, makes a quarter of a circle around to $iR$ and back to $0$, properly indented around $0$ with a quarter circle of radius $\delta$ to avoid the pole.
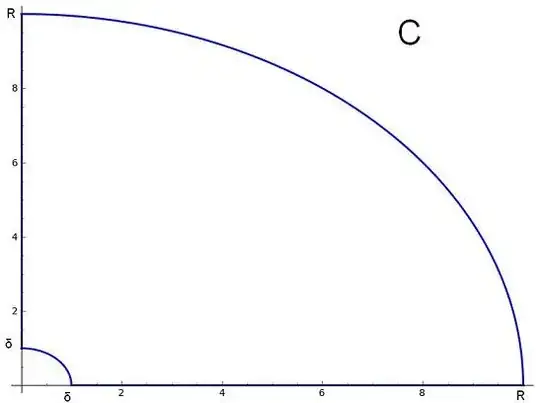
As $R \to \infty$, the integral over rounded part of the contour tends to $0$ and the part around $0$ tends to $-i\frac{\pi}{2}$ (N.B. this is $-i\frac{\pi}{2}$ of the residue at $z=0$) as $\delta \to 0$. Then by Cauchy's theorem:
$$ 0=\oint_C f(z)\,dz =\\ \int_0^\infty \frac{e^{-z+iz}}{z}\,dz -\int_0^{\infty} \frac{e^{-iz-z}}{z}\,dz - i\frac{\pi}{2} $$
And upon taking imaginary parts and solving:
$$ \frac{\pi}{4}=\int_0^\infty \frac{e^{-z}\sin(z)}{z}\,dx $$
$$\int_0^{\infty} \frac{e^{-x}\sin x}{x}\,dx=\int_0^{\infty}\int_0^{\infty} e^{-x}\sin x \,e^{-xy}\,dy\,dx=\int_0^{\infty} \int_0^{\infty} e^{-x(1+y)}\sin x\,dx\,dy$$ From integration by parts or otherwise, one can show that: $$\int_0^{\infty}e^{-x(1+y)}\sin x\,dx=\frac{1}{1+(1+y)^2}$$ Hence $$\int_0^{\infty} \int_0^{\infty} e^{-x(1+y)}\sin x\,dx\,dy=\int_0^{\infty} \frac{dy}{1+(1+y)^2}=\left(\arctan(1+y)\right|_0^{\infty}=\boxed{\dfrac{\pi}{4}}$$
$\newcommand{\+}{^{\dagger}}% \newcommand{\angles}[1]{\left\langle #1 \right\rangle}% \newcommand{\braces}[1]{\left\lbrace #1 \right\rbrace}% \newcommand{\bracks}[1]{\left\lbrack #1 \right\rbrack}% \newcommand{\ceil}[1]{\,\left\lceil #1 \right\rceil\,}% \newcommand{\dd}{{\rm d}}% \newcommand{\down}{\downarrow}% \newcommand{\ds}[1]{\displaystyle{#1}}% \newcommand{\equalby}[1]{{#1 \atop {= \atop \vphantom{\huge A}}}}% \newcommand{\expo}[1]{\,{\rm e}^{#1}\,}% \newcommand{\fermi}{\,{\rm f}}% \newcommand{\floor}[1]{\,\left\lfloor #1 \right\rfloor\,}% \newcommand{\half}{{1 \over 2}}% \newcommand{\ic}{{\rm i}}% \newcommand{\iff}{\Longleftrightarrow} \newcommand{\imp}{\Longrightarrow}% \newcommand{\isdiv}{\,\left.\right\vert\,}% \newcommand{\ket}[1]{\left\vert #1\right\rangle}% \newcommand{\ol}[1]{\overline{#1}}% \newcommand{\pars}[1]{\left( #1 \right)}% \newcommand{\partiald}[3][]{\frac{\partial^{#1} #2}{\partial #3^{#1}}} \newcommand{\pp}{{\cal P}}% \newcommand{\root}[2][]{\,\sqrt[#1]{\,#2\,}\,}% \newcommand{\sech}{\,{\rm sech}}% \newcommand{\sgn}{\,{\rm sgn}}% \newcommand{\totald}[3][]{\frac{{\rm d}^{#1} #2}{{\rm d} #3^{#1}}} \newcommand{\ul}[1]{\underline{#1}}% \newcommand{\verts}[1]{\left\vert\, #1 \,\right\vert}$ \begin{align} &\color{#00f}{\large\int_{0}^{\infty}{\expo{-x}\sin\pars{x} \over x}\,\dd x} =\int_{0}^{\infty}\expo{-x}\pars{\half\int_{-1}^{1}\expo{\ic kx}\,\dd k} =\half\int_{-1}^{1}\int_{0}^{\infty}\expo{\pars{\ic k - 1}x}\,\dd k \\[3mm]&=\half\int_{-1}^{1}{1 \over 1 - \ic k}\,\dd k =\int_{0}^{1}{\dd k \over 1 + k^{2}} = \arctan\pars{1} =\color{#00f}{\Large{\pi \over 4}}\ \ \ \ \end{align}
Double Integral $$ \begin{aligned}\int_0^{\infty} \frac{e^{-x} \sin x d x}{x} = & \int_0^{\infty} e^{-x}\left(\int_0^1 \cos (x y) d y\right) d x \\ = & \int_0^1 \int_0^{\infty} e^{-x} \cos (x y) d x d y \\ = & \int_0^1 \frac{1}{y^2+1} d y \\ = & {\left[\tan ^{-1} y\right]_0^1 } \\ = & \frac{\pi}{4} \end{aligned} $$
Recognizing $\frac1{x}$ as the Laplace transform of $1$, the given integral can be rewritten as a double integral:
$$\mathcal I=\int_0^\infty\frac{e^{-x}\sin x}{x}\mathrm dx=\int_0^\infty e^{-x}\sin x\left(\int_0^\infty e^{-xt}\mathrm dt\right)\mathrm dx$$ $$=\int_0^\infty\int_0^\infty e^{-tx}\cdot e^{-x}\sin x\mathrm dt\mathrm dx$$
Using Fubini’s theorem, $$\mathcal I=\int_0^\infty\int_0^\infty e^{-tx}\cdot e^{-x}\sin x\mathrm dx\mathrm dt$$ $$=\int_0^\infty\int_0^\infty e^{-x(t+1)}\sin x\mathrm dx\mathrm dt$$ $$=\int_0^\infty\frac{\mathrm dt}{(t+1)^2+1}$$ $$=\lim_{a\to\infty}\left[\tan^{-1}(t+1)\right]_0^a$$ $$=\frac\pi4$$
http://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=Integrate[%28e^-x*Sin[x]%2Fx%29%2C{x%2C0%2CInfinity}Ans = Pi/4=0.785398. In case you don't want to use limits and make it indefinite than use "Integrate[(e^-x*Sin[x]/x)]". This is not step by step solution obviously but may be helpful to you. – Pankaj Sejwal Jun 18 '12 at 10:17