Let $A$ has size $m\times n$ (more general), $y=A x$, $y=(y_1, y_2, \cdots y_m)$. Let $s=\sum_{i=1}^n x_i$
Then $$H(y)= H(y \mid s) + H(s) - H(s \mid y) \tag{1}$$
and we can bound:
$$ H(y \mid s) \le H(y) \le H(y \mid s) + H(s) \tag{2} $$
To compute, $H(y \mid s)$, note that while $y=(y_1, y_2, \cdots y_m)$ are not independent, they are independent if conditioned on $s$. Hence
$$H(y \mid s) = m \, H(y_1 \mid s)$$
Further, $y_1 |s \sim B(s,1/2)$ (Binomial), and $s$ is also Binomial $B(n,1/2)$ Hence
$$H(y \mid s) = m \sum_{s=0}^n \frac{1}{2^n}{n \choose s} h_B(s) \tag{3}$$
$$H(s) = h_B(n) \tag{4}$$
where $$h_B(t)= - \frac{1}{2^t} \sum_{k=0}^t {t\choose k} \log\left(\frac{1}{2^t}{t \choose k}\right) = t - \frac{1}{2^t} \sum_{k=0}^t {t \choose k} \log\left({t \choose k}\right) \tag{5}$$ is the entropy of a Binomial of size $t$ and $p=1/2$.
(all logs are in base $2$ here).
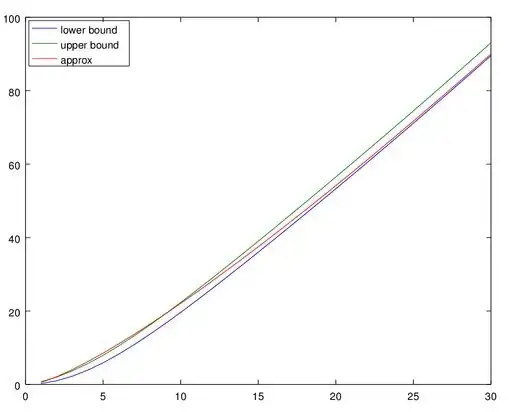
Expressions $(3)$ $(4)$, together with $(2)$, provide exact bounds. We can obtain an approximation by taking the central term in $(3)$ and using the asymptotic $h_B(t) \approx \frac{1}{2} \log(t \, \pi e /2)$. We then get
$$H(y|s) \approx \frac{m}{2} \log(n \pi e /4) \tag{6}$$
$$H(s) \approx \frac{1}{2} \log(n \pi e /2) \tag{7}$$
This strongly suggests that, when $m=n$, $H(y)$ grows as $\frac{n}{2} \log(n)$
The graps shows both bounds and the approximation $(6)$ for the lower bound.