This the answer that was accepted for the arrangement problem of a library:
we have books with heights $H_n,$ $1 \le n \le N$ and widths $W_n,$ with heights in ascending order for each book, and we want to group them into shelves.
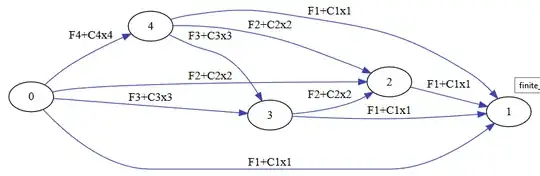
Reuse these numbers for solution nodes $n,$ where that node represents a solution state "all books $i \le n$ have been shelved." We will therefore start at node $0$ and seek to get to node $N$ by the shortest path with Dijkstra's algorithm. These nodes are the vertices of our graph.
We then draw from node $i$ to any node $j \gt i$ a directed edge which assumes that all of those intermediary books will be shelved with one shelf, i.e. the length of this edge is $$L_{ij} = F_j + C_j~\sum_{n=i+1}^j W_n,$$where I have assumed that when you were saying the cost of the sum was $F_i + C_i x_i$ the subscript $i$ on the $x_i$ was totally meaningless.
Dijkstra's algorithm will then give us a shortest-length path to node $N.$
With such an array, showing how many books do we have of length $H_i$ with $L_i$ meters of documents of $type \ i$, and the cost of storing such documents: $F_i$ a fixed command cost and $C_i$ the varying cost accorfing to $x_i$ the length of documents we would store within it,
\begin{array}{|c|rr} i & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4\\ \hline H_i & 12\,\mathrm{cm} & 15\,\mathrm{cm} & 18\,\mathrm{cm} & 23\,\mathrm{cm}\\ L_i & 100\,\mathrm{cm} & 300\,\mathrm{cm} & 200\,\mathrm{cm} & 300\,\mathrm{cm} \\ \hline F_i & 1000€ & 1200€ & 1100€ & 1600€ \\ C_i & 5€/\mathrm{cm} & 6€/\mathrm{cm} & 7€/\mathrm{cm} & 9€/\mathrm{cm}\\ \end{array}
The graph is:
My question is: why should we use a Djikstra algorithm? We don't have any circuits and we can't go backward. Therefore, shouldn't we use Bellman-Kalaba algorithm?