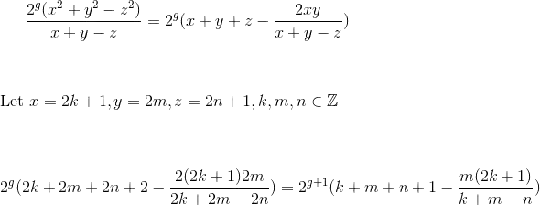To begin with note that if you a solution $x,y,z,G$ and an odd number U then clearly $Ux,Uy,Uz,G$ is a solution as well.
Thus we can add the stipulation that we are looking for tuples $x,y,z$ that do not share a common odd factor $U$.
We consider the case of $G > 0$ first.
In that case it becomes clear (through some factoring) that
$$ 2^{g} \frac{2xy}{x + y - z} $$
Must be an odd number. Now since $y$ is an even number it is evident that $y$ can be expressed as $2^rL$ for some odd number L. Therefore we can re-write our expression as
$$ 2^{g + r + 1} \frac{xL}{x + 2^rL - z} $$
So a process for finding solutions becomes apparent. Select a value g and then select a value y. Decompose $y$ into $2^rL$ for odd L. Find a pair of odd numbers (x - z) that do no share factors with L such that $2^{g + r + 1} = x - z + 2^rL$
Which can be done easily by first solving for $x - z$ as a single numerical variable $Q$ and then partitioning this $Q$ into independent $x$ and $z$ components and then consider multiples of $x,y,z$ by an odd number $U$
I don't know if this characterizes all solutions for $G > 0 $ but it is worth exploring the algorithm.
Now if $G = 0$
$$x + y + z - \frac{2xy}{x + y - z}$$
Needs to be odd. Note that since $x,z$ are odd integers and $y$ is even it follows that:
$$\frac{2xy}{x + y - z}$$
Must be odd which implies that (after decomposing y)
$$\frac{2^{r+1}xL}{x - z + 2^{r}L}$$
Must be odd given odd numbers x,L,z. Again an algorithm has been generated. Selected a value y, from this y compute the decomposition, from which to select a Q such that $Q + y = 2^{r+1}$ and then decompose Q into the difference of 2 odd numbers $x,z$ such that $x,z,L$ do not share common factors.
Curiously this process is exactly the same thing as the previous process.