The classical Euler-Mascheroni Constant is
$$ \gamma = \lim_{n \to \infty} \left( \sum_{k=1}^n \frac{1}{k} - \ln(n) \right) $$
I'm trying to extend $\gamma$ to higher dimensions denoted by $\gamma_n$ and am curious if a higher dimensional generalization of the Euler-Mascheroni Constant is valid?
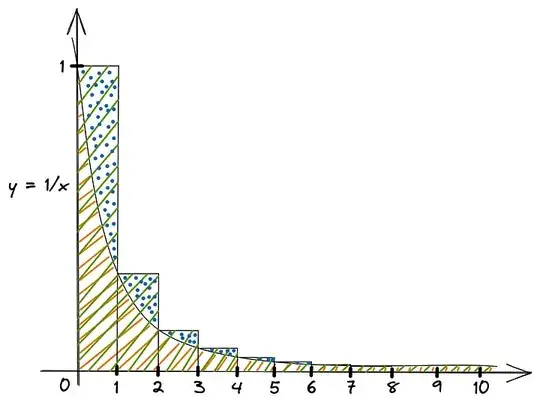
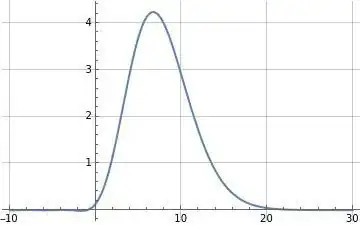
$2D$ Representation (Classical $\gamma$)
Graphical representation of $\gamma$
Green Bars: Represent the harmonic series $\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{1}{k}$
Orange Area Under Curve: Represents $\int_{1}^{n} \frac{1}{x} \, dx = \ln(n)$
Blue Dotted Area: Represents the difference to give the Euler—Mascheroni constant
$$ \underbrace{\gamma}_{\text{blue area}} = \lim_{n \to \infty} \left( \underbrace{\sum_{k=1}^n \frac{1}{k}}_{\text{green area}} - \underbrace{\ln(n)}_{\text{orange area}} \right) $$
Applying similar geometric methods, we can extend it to higher dimensions.
For example, consider the following $3D$ representation.
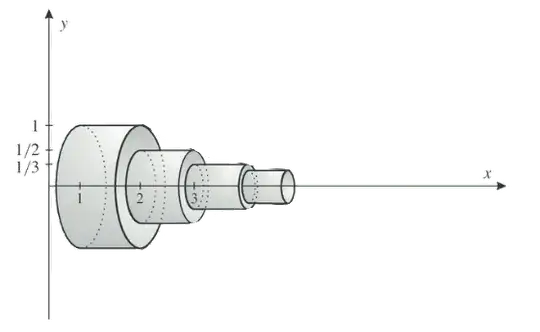
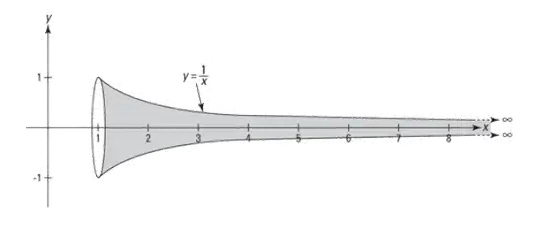
$3D$ Representation ($\gamma_3$)
Visualize revolving the bars around the $x$-axis to form Gabriel's Wedding Cake (an infinite stack of cylinders with volume $\frac{\pi^3}{6}$) and revolve the curve $y=\frac{1}{x}$ to form Gabriel's Horn (volume $\pi$). The difference between these two volumes represents the Euler—Mascheroni constant $\gamma_3=\frac{\pi^3}{6} - \pi$.
Gabriel's Cake
Gabriel's Horn
Furthermore, each $n$-dimension has its own distinct Euler-Mascheroni constant:
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|} \hline \textbf{n-dimension} & \mathbf{\gamma_n} & \mathbf{\approx} \\ \hline 3 & \hspace{5pt} \pi \left( \zeta(2) - 1 \right) \hspace{5pt} & 2.0261201264...\\ \hline 4 & \hspace{5pt} \frac{2}{3} \pi \left( 2 \, \zeta(3) - 1 \right) \hspace{5pt} & 2.9407690791... \\ \hline 5 & \hspace{5pt} \frac{1}{2} \pi^2 \left( \zeta(4) - \frac{1}{3} \right) \hspace{5pt} & 3.6961170085... \\ \hline 6 & \hspace{5pt} \frac{8}{15} \pi^2 \left( \zeta(5) - \frac{1}{4} \right) \hspace{5pt} & 4.1422216722... \\ \hline 7 & \hspace{5pt} \frac{1}{6} \pi^3 \left( \zeta(6) - \frac{1}{5} \right) \hspace{5pt} & 4.2237941871... \\ \hline 8 & \hspace{5pt} \frac{16}{105} \pi^3 \left( \zeta(7) - \frac{1}{6} \right) \hspace{5pt} & 3.9767533569... \\ \hline \end{array}
Definitions
- $\gamma$ - classical Euler-Mascheroni constant.
- $\zeta(s)$ - Riemann zeta function.
- $\Gamma(s)$ - Gamma function.
- $V_c$ - Volume of Gabriel's Wedding Cake in $n$-dimensions.
- $V_h$ - Volume of Gabriel's Horn in $n$-dimensions.
- $\gamma_n$ - Euler-Mascheroni constant in $n$-dimensions.
Conjecture
For dimension $n \ge 3$, the $n$-dimensional Euler-Mascheroni constant is:
$$ \gamma_n=\frac{\pi^{\frac{n-1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left(\dfrac{n+1}{2}\right)} \left(\zeta(n-1)-\dfrac{1}{n-2}\right) $$
Proof
The volume of an $(n-1)$-dimensional Hyper-sphere with radius $R$ is
$$ V_{n-1}(R) = \frac{\pi^{\frac{n-1}{2}} R^{n-1}}{\Gamma\left( \frac{n+1}{2} \right)} $$
The volume of an $n$-dimensional Hyper-cylinder is
$$ V_{n}(R) = \underbrace{V_{n-1}(R)}_{\text{base}} \times \underbrace{h}_{\text{height}} $$
The volume of Gabriel's Wedding Cake $V_{c}$ with $R_k = \frac{1}{k}$ and $h=1$ is
\begin{align*} V_c &= \sum_{k=1}^{\infty} V_n(R_k) \\ &= \sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \frac{\pi^{\frac{n-1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left(\frac{n+1}{2}\right)} \left(\frac{1}{k}\right)^{n-1} \\ &= \frac{\pi^{\frac{n-1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left(\frac{n+1}{2}\right)} \sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \frac{1}{k^{n-1}} \\ &= \frac{\pi^{\frac{n-1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left(\frac{n+1}{2}\right)} \zeta(n-1) \end{align*}
The volume of the $n$-dimensional Gabriel's Horn $V_h$
\begin{align*} V_h &= \int_1^\infty V_{n-1}\left( \frac{1}{x} \right) \, dx \\ &= \frac{\pi^{\frac{n - 1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left( \frac{n + 1}{2} \right)} \int_1^\infty \frac{1}{x^{n - 1}} \, dx \\ &= \frac{\pi^{\frac{n - 1}{2}}}{\, \Gamma\left( \frac{n + 1}{2} \right)} \left(\frac{1}{n - 2} \right) \end{align*}
The $n$-dimensional Euler-Mascheroni constant $\gamma_n$ is defined as
\begin{align*} \gamma_n &= V_c - V_h \\ &= \frac{\pi^{\frac{n-1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left( \frac{n+1}{2} \right)} \zeta(n-1) - \frac{\pi^{\frac{n - 1}{2}}}{\, \Gamma\left( \frac{n + 1}{2} \right)} \left(\frac{1}{n - 2} \right) \\ &= \frac{\pi^{\frac{n - 1}{2}}}{\Gamma\left( \dfrac{n + 1}{2} \right)} \left( \zeta(n - 1) - \dfrac{1}{n - 2} \right) \quad \blacksquare \end{align*}