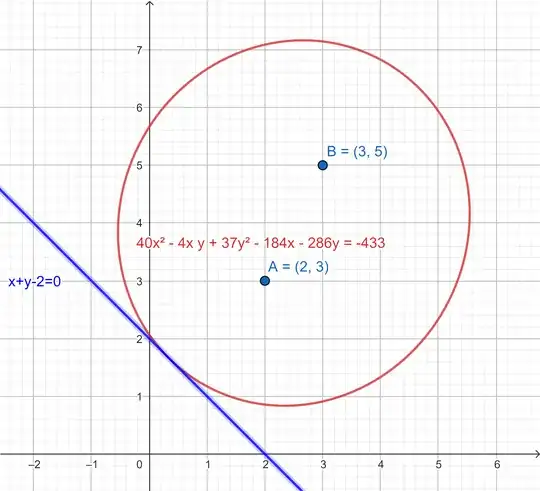
Let $F_1 = (2,3), F_2 = (3,5)$. At a point $P = (x,y)$ on the line $x+y=2$, the normal to this line bisects the angle between $PF_1$ and $PF_2$, that is, the line acts as a mirror for the ray coming out of $F_1$ towards the line, and reflects it at $P$ back into the ellipse to pass through $F_2$. The point $P$ can be found based on this reflection process, as follows. Reflect $F_1$ about the line, and connect the reflected point $F_1'$ with $F_2$ to find the intersection of this line segment $F_1' F_2$ with the line $x+y=2$.
The reflection of $F_1(2,3)$ into the line $x+y=2$ is the point $F_1'(x',y')$ such that the midpoint of $F_1 F_1'$ lies on the line $x+y=2$, and the segment $F_1 F_1'$ is perpendicular to the line $x + y = 2 $. The first condition means
$ \dfrac{1}{2} [ (2 + x') + (3 + y') ] = 2 $
And the second condition means
$ \dfrac{ y' - 3}{x' - 2} = 1 $
So that, now we have the following linear system in $x'$ and $y'$
$ x' + y' = -1 $
$ x' - y' = -1 $
The solution is, by inspection, $F_1' = (x',y') = (-1, 0) $
Now the line segment $F_1' F_2 $ has the equation
$ y = \dfrac{5}{4} \ ( x + 1 ) $
The intersection of this line with $x + y = 2$ is the point $P = (\dfrac{1}{3}, \dfrac{5}{3} ) $
This point is on the ellipse, therefore,
$ 2 a = \| PF_1 \| + \| PF_2 \| = \dfrac{1}{3}\bigg( \sqrt{ 5^2 + 4^2} + \sqrt{ 8^2 + 10^2 } \bigg) = \sqrt{41} $
And
$| F_1 F_2 | = 2 c = \sqrt{ 1^2 + 2^2} = \sqrt{5} $
but
$ c = a e $
So the eccentricity $e$ is
$ e = \dfrac{c}{a} = \dfrac{2c}{2a} = \dfrac{ \sqrt{5} }{\sqrt{41}} $
Hence,
$ \dfrac{1}{e^2} = \dfrac{ 41 }{5} $
This Sage worksheet depicts the ellipse and the tangent line $x+y=2$.