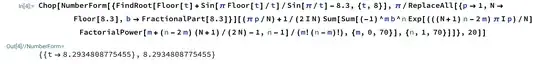$\def\f{\lfloor r\rfloor}$From the Desmos link, $t$ is the “number of sides” of a continuously growing polygon with perimeter $p$ and side length $s$. Set $\frac ps=r,\frac\pi t=x$. Rewriting with a Chebyshev U series, an equivalent problem is solving: $$\{r\} =\text U_{\f-1}(\cos(x)))=\sum_{n=0}^{\left\lfloor\frac{r-1}2\right\rfloor}\frac{(-1)^n \Gamma(\f-n)}{\Gamma(\f-2n)n!} (2\cos(x))^{\f-2n-1} $$ Which means inverting a $\cos(x)$ polynomial of degree $\begin{cases}\f-1&\f\text{ even}\\\frac{\f-1}2&\f\text{ odd}\end{cases}$. There are elementary inverses for the $\f=1,\dots,5,7,9$ cases, of which $\f=7$ and $\f=9$ do not show major simplifications in radical form, while the $\f=6,11$ cases have a single series quintic equation solution here. The following series solution can be used for $\f=8,10,12,13,\dots$ as those cases do not simplify. Next, notice $\lfloor r\rfloor =\lfloor t\rfloor$, so the fractional part $\{r\}=r-\lfloor t\rfloor$appears: $$p = s\left( \lfloor t\rfloor +\frac{\sin\left(\frac{\pi \lfloor t\rfloor}{t}\right)}{\sin\left(\frac{\pi}t\right)}\right)\iff \{r\} \sin\left(x\right) =\sin\left(\f x\right)$$ Now we use >Is there any way to solve for $k$, given $\beta \sin (k-k N)-\sin (k N+k)=0$?: $$\beta\sin ((1-N)k)=\sin((1+N)k)\implies k_p=\frac{\pi p}{N+1}+\frac1{2i(N+1)}\sum_{n=1}^\infty\sum_{m=0}^{n-1} e^\frac{2\pi i p((N-1)m+n)}{N+1}\frac{(-1)^m \beta^n}{m!(n-m)!}\left(\frac{n-2m}{N+1}+m-1\right)^{(n-1)}$$ for the $p$th real root with factorial power $u^{(v)}$ and substitute $(1-N)k=x,\frac{1+N}{1-N}=\f,\beta=\{r\},p=1$. Therefore: $$\boxed{r=\lfloor t\rfloor +\frac{\sin\left(\frac{\pi \lfloor t\rfloor}{t}\right)}{\sin\left(\frac{\pi}t\right)}\implies \frac1t=\frac1\f+\frac1{2i \pi\f}\sum\limits_{n=1}^\infty\sum\limits_{m=0}^\infty \exp\left(\frac{\pi i(n (\f+1)-2m)}\f\right)\frac{(-1)^m\{r\}^n}{m!(n-m)!}\left(\frac{((\f+1)(n-2m)}{2\f}+m-1\right)^{(n-1)}}$$ shown here:
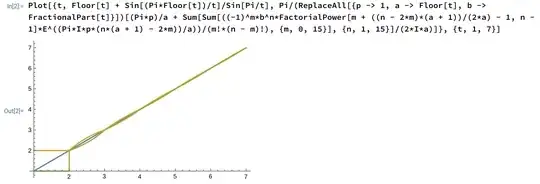
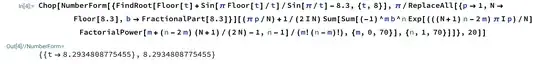
One may use Wolfram Cloud etc. with the above series, or FindRoot, and plug it into the area function to find the area of a certain polygon given its $\frac ps$ value.