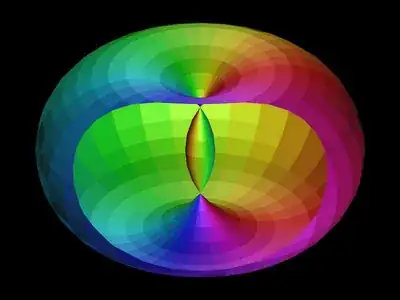
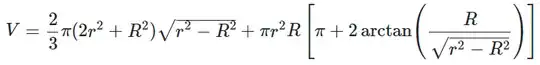The spindle torus should be treated as two dependent surfaces. The second image in the question is a screenshot from Peter Lynch's ThatsMaths blog https://thatsmaths.com/2021/02/11/apples-and-lemons-in-a-doughnut/
In 2022, I wrote a theoretical particle physics manuscript where I needed a formal citation for the area and volume formulas provided in Peter Lynch's blog. I contacted Peter Lynch and asked from where he obtained those formulas. He replied that he derived them himself and was unaware of any modern references. So we collaborated and wrote an appendix to our January 23, 2023 publication "Ground State Quantum Vortex Proton Model" in the peer-reviewed journal Foundations of Physics.
What follows, in quotations, is an abridged version of that appendix. Note, that relative to the question, the symbols $R$ and $r$ have been swapped. For the lemon, $\phi_m=\cos^{-1}(r/R)$. For the apple, $\phi_m=\pi-\cos^{-1}(r/R)$.
"A spindle torus consists of an inner lemon surface and an apple outer surface. The lemon is generated by rotating an arc of half-angle $\phi_m$ less than $\pi/2$ about its chord. Note that $\phi$ denotes latitude, as used in geophysics. It does not denote the azimuthal angle of conventional physics spherical coordinates. The surface area is given by
\begin{eqnarray}
A=2\pi R^2\int_{-\phi_m}^{\phi_m}(\cos\phi-\cos\phi_m)d\phi
\label{eq:appone}.
\end{eqnarray}
The volume is given by
\begin{eqnarray}
V=\pi R^3\int_{-\phi_m}^{\phi_m}(\cos\phi-\cos\phi_m)^2\cos\phi d\phi
\label{eq:apptwo}.
\end{eqnarray}
These integrals can be evaluated analytically, giving
\begin{eqnarray}
A=4\pi R^2(\sin\phi_m-\phi_m\cos\phi_m)
\label{eq:appthree}
\end{eqnarray}
\begin{eqnarray}
V=\tfrac{4}{3}\pi R^3\left[\sin^{3}\phi_m-\tfrac{3}{4}\cos\phi_m(2\phi_m-\sin2\phi_m)\right]
\label{eq:appfour}
\end{eqnarray}
The apple is generated by rotating an arc of half-angle $\phi_m$ greater than $\pi/2$ about its chord. Note that the above equations are valid for both the lemon and apple."
The area integral may be evaluated as a straightforward definite integral of the cosine function. The volume integral may be evaluated by expanding the square. The volume formula is then the sum of definite integrals of the cosine and cosine-squared functions.
The final volume formula, provided in the question, is numerically identical to the volume formula, provided above, when applied to the apple surface. Both of these volume formulas are for the entire volume inside the surface in question. This implies that the calculated apple volume includes the lemon volume.