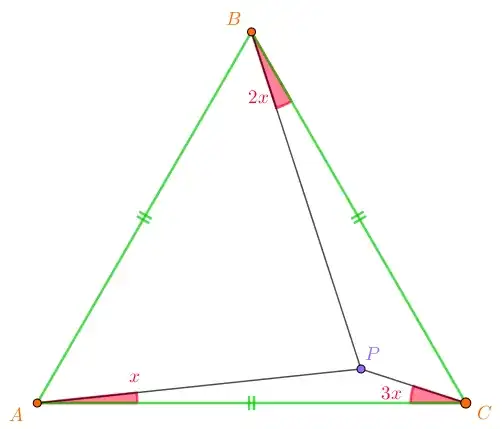
We have a point $P$ inside the equilateral triangle $\triangle ABC$, such that $\angle PAC = x$, $\angle PCA = 3x$ and $\angle PBC = 2x$. Find the value of $x$ in degrees.
I solved the problem in GeoGebra, and I know the value for $x$ is $6°$. Also I solved this problem by using the Trigonometry Ceva's Theorem: $$ \sin(60°-2x)\sin(x)\sin(60°-3x)=\sin(2x)\sin(60°-x)\sin(3x) $$ Where I used WolframAlpha to get $x=6°$.
However, I'm looking for a geometric solution. This is what I have reacher so far.

First, draw the circle that lies over $B$, $P$ and $C$. Then extend sides $AB$ and $AC$ to get point $E$ and $D$ (we have another equilateral triangle $\triangle AED$). Due to properties of angles inscribed in a circle $\angle PDC = 2x$ and $\angle PED = 3x$. Then trace the bisector $DG$, we get that $\angle GDP=30°-2x$ and $\angle PGD = 3x$. Here I got stuck. I think, I should proof that $GP = PD$, but I don't know how.
I would appreciate any contribution to this solution, or if you have a different approach and solution I would glad to hear it.