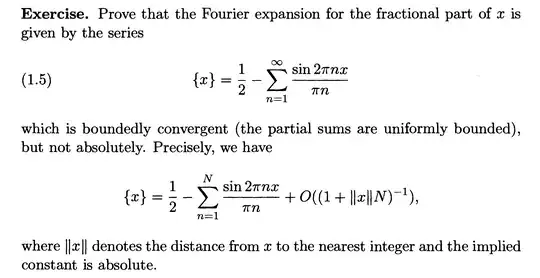
I'd like to prove the error estimate for the factional part of $x$ as given above.
To begin with, we apply the Abel's formula and get
$$(1):\left|\sum_{n=N+1}^M \frac{\sin(2\pi n x) }{n}\right|=\left|\frac {\sum_{n=N+1}^{M} \sin(2\pi n x)}{M}+ \\ \sum_{k=N+1}^{M-1} \left (\sum_{k=1}^n \sin(2\pi k x) \right)(\frac{1}n- \frac{1}{n+1}) \right|$$
Moreover, we have $$(2): \left|\sum_{n=N+1}^M \sin(2\pi n x) \right|=\left| \frac{\cos(2\pi Nx)-\cos(2\pi Mx)}{2\sin(\pi x)} \right| \\= \left | \frac{\sin(\pi (N-M)x)\sin(\pi (M+N)x)}{\sin(\pi x)} \right |.$$
I hope my calculation is correct. If so, how do I conclude from those equations that (as $M \to \infty$) the error is $O((1+\|x\|N)^{-1})$, as $x$ approaches any integer and $N\to \infty$?
I think I am able to see that when $x$ is a fix number away from any integer, then the error is $O(1/N)$. However, I don't know how to handle this when $x$ is considered.
There is solution to the same question with very different method https://math.stackexchange.com/a/57207/185631