Given a $n \times n$ grid with some walls and two cells $a$ and $b$, I want to compute the non-homotopics paths from $a$ to $b$ on this grid. A path is a sequence of adjacent cells (diagonal does not count) such that from one cell to another, we never go through a wall. We also ask our path to be non-looping, that is that they do not cross a given cell twice. Two paths are homotopic if we can deform one into another while still having valid paths through the deformation. A wall is a boundary between two adjacent cells.
More formally, two paths $p$ and $q$ are homotopic if there exists a sequence of paths $p_0,p_1,\dots,p_n$ such that $p_0 = p$, $p_n =q$ and for all pair of paths $p_i$ and $p_{i+1}$, every cell of one of those paths is adjacent to a cell in the other path. Equivalently (I believe) it means that the loop formed by following $p$ from $a$ to $b$ and then $q$ from $b$ to $a$ does not contain walls. This forms an equivalence relation on non-looping paths. I would like an algorithm that outputs one path from each equivalence class.
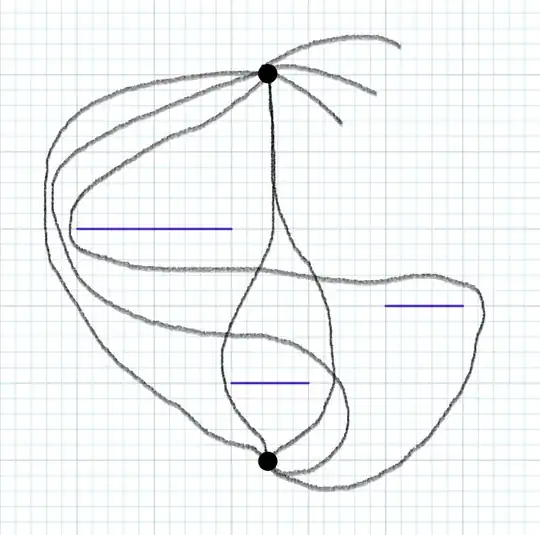
Here is an example of some non-homotopic pathes with three walls. The setting is discrete but this was easier to draw like this. Taking any two path on this image, we see that there is always a wall inside the shape they create.
From there, what I am looking for is an algorithm such that, given $n$ and a list with the positions of the walls computes a list containing a path (ideally the smallest) in each class of homotopic paths.