As Chi say to you, if you have in a program two operations, one $\mathcal{O}(log{}n)$ and another $\mathcal{O}(n) $ you must take a superior bound, and your result will be $\mathcal{O}(n)$ in this case.
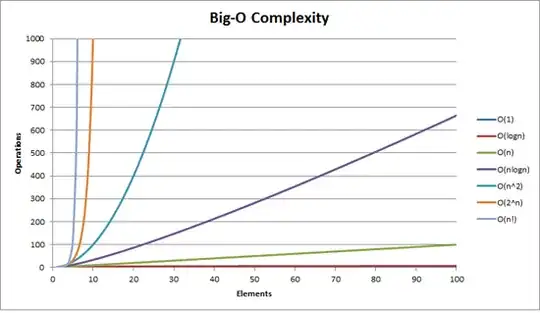
you can see here the complexity graph.
If you say, that one operation take time $\mathcal{O}(n) $ , and nobody other operations take more of this, you can be at least $\mathcal{O}(n) $ time complexity.
If just one operation are over $\mathcal{O}(n) $, the complexity will be change in new bound (and so on).
P.s Sum two bound, will maintain the most higher, multiply increse time complexity, like two neasted loop of $\mathcal{O}(n)$ will give you $\mathcal{O}(n^2)$ complexity.
I hope that this will help you.
