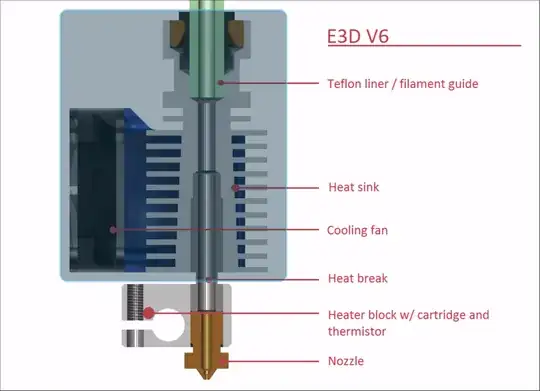
The heat sink is there to prevent too much heat creep from the hot end up into the the cold end or bowden tube (depending on printer type). The filament in these sections needs to remain firm, so it can be driven into and through the extruder. Heat rises and spreads, even through solids, and the printer will not function properly if enough heat rises into those components for filament to soften.
So the hot end needs to be hot... but then we need a fairly quick and clean break where temperatures are back to "normal" again. Heat sinks (and even fans) can help with this. You'll further notice the use of a heat break in the diagram, and all the heat sink material is on the other side of the break from the heater block.
It's further worth noting print head mass contributes directly to issues like ringing, and has an inverse effect on both quality and speed... the lighter the print head, the better things will generally work out. Printer designers would therefore love to be able to remove heavy heat sink material from the print head, as that would also allow gains in both speed and quality... but they can't, because this really is absolutely necessary for the printer to function properly.