The easiest and most straight forward iterative method would be the Projected Gradient Descent.
Projection onto Linear Equality Equation
The Projected Gradient Descent requires a projection step onto the Linear Equation constraint.
The problem is given by:
$$ \arg \min_{x} \frac{1}{2} \left\| x - y \right\|_{2}^{2}, \quad \text{subject to} \quad B x = d $$
From the KKT Conditions one could see the result is given by:
$$ \hat{x} = y - {B}^{T} \left( B {B}^{T} \right)^{-1} \left( B y - d \right) $$
Full derivation is given at Projection of $ z $ onto the Affine Set $ \left\{ x \mid A x = b \right\} $.
Now, all needed is to integrate that into the Projected Gradient Descent framework.
%% Solution by Projected Gradient Descent
hObjFun = @(vX) (0.5 * sum((mA * vX - vB) .^ 2));
hProjFun = @(vY) vY - (mB.' * ((mB * mB.') \ (mB * vY - vD)));
vObjVal = zeros([numIterations, 1]);
mAA = mA.' * mA;
vAb = mA.' * vB;
vX = mB \ vD; %<! Initialization by the Least Squares Solution of the Constraint
vX = hProjFun(vX);
vObjVal(1) = hObjFun(vX);
for ii = 2:numIterations
vX = vX - (stepSize * ((mAA * vX) - vAb));
vX = hProjFun(vX);
vObjVal(ii) = hObjFun(vX);
end
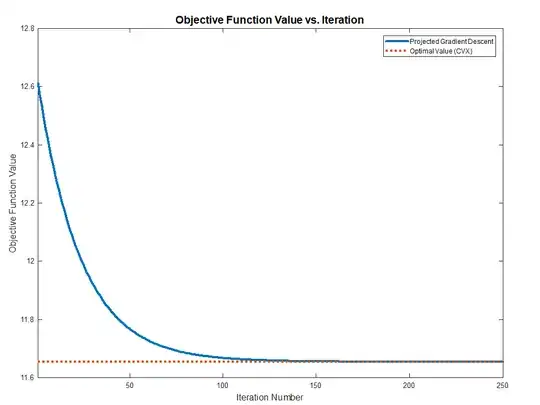
The full code, including validation using CVX, can be found in my StackExchange Mathematics Q1596362 GitHub Repository.
