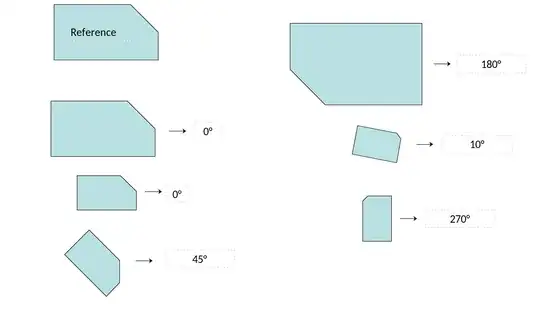
valentas pointed me in the right direction and the following function estimateAffinePartial2D() from OpenCV solves almost the problem. Almost, because it assumes that the points in the source and destination coordinates are in the optimal order. See case 4 below for an example. To address this, I use a brute force approach and try all possible permutations and keep the one that leads to the smallest reprojection error.
import itertools
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
Simple triangle:
src_points = np.array([[50, 50], [100, 50], [75, 100]], dtype=np.float32)
Case 1: X translation:
dst_points = np.array([[1050, 50], [1100, 50], [1075, 100]], dtype=np.float32)
Case 2: Y translation:
dst_points = np.array([[50, 1050], [100, 1050], [75, 1100]], dtype=np.float32)
Case 3: 180° rotation:
dst_points = np.array([[100, 100], [50, 100], [75, 50]], dtype=np.float32)
Case 4: 180° rotation with different point indices:
dst_points = np.array([[50, 100], [75, 50], [100, 100]], dtype=np.float32)
best_error = None
best_angle = None
best_permutation = None
for permutation in itertools.permutations(dst_points):
np_permutation = np.array(permutation)
# Estimate affine transformation matrix (rotation + translation)
transformation_matrix, inliers = cv2.estimateAffinePartial2D(src_points, np_permutation)
if transformation_matrix is not None:
# Extract the rotation matrix part from the transformation matrix
cos_theta = transformation_matrix[0, 0]
sin_theta = transformation_matrix[1, 0]
rotation_angle_radians = math.atan2(sin_theta, cos_theta)
rotation_angle_degrees = np.degrees(rotation_angle_radians)
# Calculate reprojection error (Euclidean distance between transformed points and destination points)
# Only using inliers to calculate the error
inlier_points = src_points[inliers]
# Apply the transformation to the inlier points
transformed_points = cv2.transform(inlier_points, transformation_matrix)[0]
# Now calculate the reprojection error (Euclidean distance) for inliers
reprojection_errors = np.linalg.norm(transformed_points - np_permutation[inliers], axis=1)
reprojection_error = np.mean(reprojection_errors)
print(f"reprojection_error: {reprojection_error}")
if best_error is None or best_error > reprojection_error:
best_permutation = permutation
best_error = reprojection_error
best_angle = rotation_angle_degrees
else:
print("Transformation estimation failed.")
print()
print(f"Best permutation: {permutation}")
print(f"Best error: {best_error}")
print(f"Best angle: {best_angle}")
I wonder now if there is a better solution than the brute-force approach.