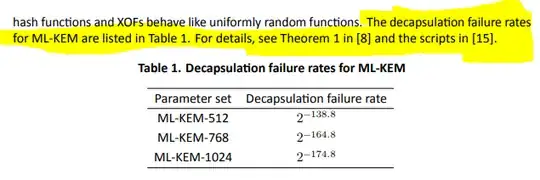
As highlighted in your question, scripts for the computation can be found at reference [15], specifically https://github.com/pq-crystals/security-estimates/blob/master/Kyber_failure.py which uses several functions from the additional file https://github.com/pq-crystals/security-estimates/blob/master/proba_util.py
Essentially, because the building blocks are small centred binomial distributions, it is possible to naively build up a modest, discretised, distribution function for integer value
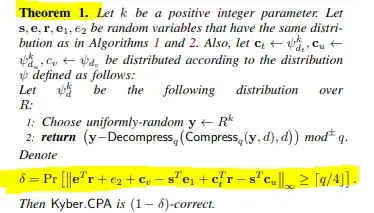
$$\mathbf e^T\mathbf r+e_2+ c_v-\mathbf s^T\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_t^T\mathbf r-\mathbf s^T\mathbf c_u.$$
as the sum of products of distributions of integer values (with a little judicious rounding where probabilities less than $2^{300}$ are ignored for efficiency).
Going through Kyber_failure.py line-by-line, the main action happens in this function def p2_cyclotomic_final_error_distribution(ps):
chis = build_centered_binomial_law(ps.ks) # LWE error law for the key
chie = build_centered_binomial_law(ps.ke_ct) # LWE error law for the ciphertext
chie_pk = build_centered_binomial_law(ps.ke)
the above three lines compute the probabilities for the centred binomial distribution for coefficients of $\mathbf e_1$, $\mathbf r$; $\mathbf e$, $e_2$; $-\mathbf s$ (introducing a - sign for convenience, as the coefficients are symmetric about 0, this is not an issue). For example, in the case ML-KEM 768, these should all be a dictionary with {-2: 0.0625, -1: 0.25, 0: 0.375, 1: 0.25, 2: 0, 0.625}. Note that this does not depend on $k$, $q$, nor $\psi$ just the parameter $\eta$ of the centred binomial.
Rk = build_mod_switching_error_law(ps.q, ps.rqk) # Rounding error public key
Rc = build_mod_switching_error_law(ps.q, ps.rqc) # rounding error first ciphertext
the above two lines compute the distribution of coefficients of $c_t$ and $c_u$ (again as a dictionary). Note that this is dependent on $\psi$ and hence also $q$ (though as we are computing coefficient-wise there is no dependence on $k$).
chiRs = law_convolution(chis, Rk) # LWE+Rounding error key
chiRe = law_convolution(chie, Rc) # LWE + rounding error ciphertext
these two lines compute the distributions of coefficients of $\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_u$ and $\mathbf e+\mathbf c$ using the convolution formula for the sum of two distributions
$$\mathbb P[X+Y=z]-\sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty\mathbb P[X=k]\mathbb P[Y=z-k]$$
B1 = law_product(chie_pk, chiRs) # (LWE+Rounding error) * LWE (as in a E*S product)
B2 = law_product(chis, chiRe)
and these compute the distribution of either the product of a coefficient of $(\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_u)$ with a coefficient of $-\mathbf s$ and the product of a coefficient of $(\mathbf e+\mathbf c_t)$ with a coefficient of $\mathbf r$. Here the dictionary is computed using the product of two random variables.
$$\mathbb P[XY=z]=\sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty\mathbb P[X=k]\mathbb P[Y=z/k]$$
C1 = iter_law_convolution(B1, ps.m * ps.n)
C2 = iter_law_convolution(B2, ps.m * ps.n)
these compute the distribution of $-\mathbf s^T(\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_u)$ and of $(\mathbf e+\mathbf c_t)\mathbf r$ as the sum of $mn$ of the products. Again the convolution formula is used, but in this case iteratively using an addition chain. Here is where the dependence on $k=mn$ appears.
C=law_convolution(C1, C2)
...and this computes the distribution of $-\mathbf s^T(\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_u)+(\mathbf e+\mathbf c_t)\mathbf r$. Again, the convolution formula is used.
R2 = build_mod_switching_error_law(ps.q, ps.rq2) # Rounding2 (in the ciphertext mask part)
...and this computes the distribution of $c_v$ (again depending on $\psi$ and $q$, but not $k$)
F = law_convolution(R2, chie) # LWE+Rounding2 error
...and this computes the distribution of $-\mathbf s^T(\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_u)+(\mathbf e+\mathbf c_t)\mathbf r+e_2$, again using the convolution formula. So that finally
D = law_convolution(C, F) # Final error
... computes the distribution of $c_v-\mathbf s^T(\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_u)+(\mathbf e+\mathbf c_t)\mathbf r+e_2$ which is $\mathbf e^T\mathbf r+e_2+c_v-\mathbf s^T\mathbf e_1+\mathbf c_t^T\mathbf r-\mathbf s^T\mathbf c_u$ as required.
A subsequent call to tail_probability with this distribution sums the probabilities of all dictionary entries outside the range $(-q/4,q/4)$ to give $\delta$